Understanding VLAN Trunking Protocol | CCNA Study
Understanding VLAN Trunking Protocol | CCNA Study
Understanding VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
One must first configure the switch in order to transmit traffic to a virtual local area network (VLAN). Take, for example, a scenario in which the user wishes to send a frame from the source to the destination, and the shortest path between the two locations comprises one thousand switches. In order to execute a frame of any VLAN, it is necessary to first configure the VLANs. Therefore, it is necessary to manually configure the identical VLANs on each of the one thousand switches. Unfortunately, the administrator will not be able to carry out that action. Fortunately, VTP is here to save the day.
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP): The VLAN Trunking Protocol, often known as VTP, is a proprietary protocol developed by Cisco that is utilized to ensure that consistency is maintained across the whole network. Alternatively, the user may refer to this as synchronizing the VLAN information inside the same VTP. In the VTP domain, you have the ability to add, delete, and rename virtual local area networks (VLANs), which are subsequently propagated to other switches. VTP advertising is able to be transmitted across ISL trunks as well as 802.1Q.

Requirements – VTP must fulfill certain conditions in order for switches to be able to send VLAN information to one another. These include:
- When the user wants to configure switches, the VTP version must be the same on all of those switches.
- On all of the switches, the VTP domain name must be identical.
- There must be a server that is one of the switches.
- If authentication is implemented, it should be consistent.
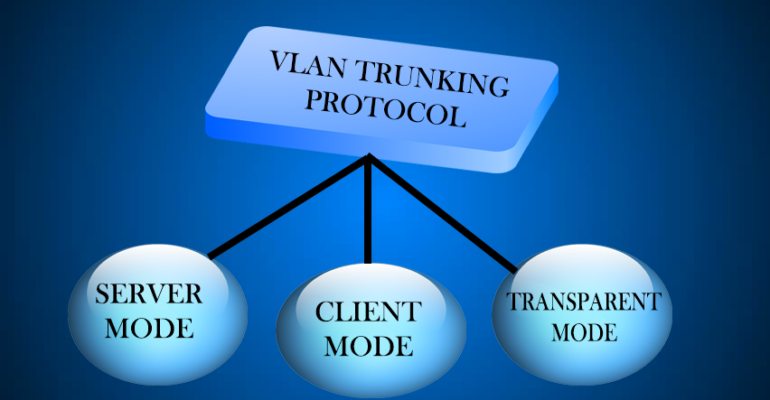
VTP modes – There are 3 modes:
- Server – By default, the switches are configured to operate in this mode. In this mode, you have the ability to establish, add, and delete virtual local area networks (VLANs). The modifications that you intend to make ought to be carried out in this mode. Whenever any modifications are made to this mode (on a specific switch), they will be broadcast to all of the switches that are part of the same VTP domain. When operating in this mode, the configuration is stored in the NVRAM.
- Configuration – Initially, the user will make the transition to the VTP server.
| Switch# config terminal
Switch(config)#vtp mode server |
The user is now required to create a VTP domain and assign a password in order to authenticate themselves.
| Switch(config)#vtp domain geeksforgeeks
Switch(config)#vtp password hardwork |
The user is now required to create a VTP domain and assign a password in order to authenticate themselves.
| Switch(config)#do should vtp password
Switch(config)#do show vtp |
- Client – The switches are able to receive the updates and also have the ability to pass the updates to other switches that are present in the same VTP domain when operating in this mode. The changes that are received here are not retained in the NVRAM, which means that all of the configurations will be lost if the switch is reset or reloaded. This means that the switches will only learn and pass on the VTP summary advertising to the other switches.
- Configuration – As a result of the fact that the switches are configured to operate in server mode by default, the user can switch it to client mode by:
| Switch(config)#vtp mode client |
- Transparent – Only the VTP summary advertising is transmitted across the trunk link when this mode is activated. Switches that operate in transparent mode have the ability to create their own local databases, which they can keep hidden from other switches. To forward the VTP summary advertising is the sole objective of the transparent mode, which does not participate in the assignment of VLANs under any circumstances.
- Configuration – Changing the mode to translucent can be done by the user using:
| Switch(config)#vtp mode transparent |
Configuration Revision Number – When it comes to a VTP packet, the configuration revision number is a 32-bit number that denotes the level of revision that has been applied. Every switch keeps a record of this configuration number to determine whether or not the information that has been received is more recent than the version that is currently in use. If the server switch makes a single adjustment to the virtual local area networks (VLANs), the configuration revision number will rise by one. When the client mode devices receive it, they compare their own configuration number with the number that they received to determine whether or not the configuration revision number that they received is the most recent in the configuration history. If the configuration number is higher than the number that the devices themselves possess, the devices will update their configuration and then transmit it to other clients that belong to the same VTP domain. If the configuration number is identical, the devices will simply transmit it to other clients that belong to the same VTP domain. Users are able to check the revision number of the configuration by:
| Switch(config)#do show vtp status |
Use VTP in an Organization: All switches are, by default, intended to function as virtual private network (VPN) servers. This architecture is suitable for limited-scope networks, in which the size of the VLAN data is relatively small, and the data may be easily stored in all switches (in NVRAM). When the NVRAM stockpiling that is important is inefficient due to the fact that it is replicated on each switch, the chairman of the organization should make a decision sooner or later. This is because the organization is very large. In the present moment, the manager of the organization ought to select a few distinctive switches and maintain them as virtual private network servers. Each and every other thing that is a part of VTP has the potential to be transformed into a client. Choosing the appropriate number of virtual private network (VPN) servers is essential in order to achieve the desired level of overt repetitiveness inside the organization.
Contemplations:
- By arranging the VTP area name on the switch that runs Cisco IOS, it is possible to build virtual local area networks (VLANs).
- When another Impetus is joined in the line of two VTP spaces, the new Impetus will retain the space name of the principal switch that sends it a synopsis ad. This occurs when the initial Impetus is joined. Making a physical change to the name of an alternate VTP area is the most effective method for joining this modification to another VTP space.
- A DTP parcel contains the VTP space name, which is transmitted by the Dynamic Trunking Convention (DTP). Consequently, if you use DTP, the storage compartment will not appear in the event that you have two ends of a connection that are located in different VTP areas. Because of this, the storage compartment will not be visible. According to this one-of-a-kind circumstance, you ought to build the storage compartment mode as on or negotiate on both sides in order to make it possible for the storage compartment to display without the need for DTP discussion comprehension.
- In the event that the location has a single VTP server and it experiences a crash, the most effective and uncomplicated method for reestablishing the activity is to switch any of the VTP clients in that location to a VTP server. The modification to the arrangement has not yet been implemented in any of the other clients, regardless of whether or not the server has crashed. Because of this, VTP functions in an appropriate manner throughout the region.
Join CCNA 200-301 Training Certification by Craw Security
At this time in Craw Security, we are moving beyond the depths of networking techniques, and you have the opportunity to participate in the useful CCNA 200-301 Certification Training in Delhi that is being provided by a skilled training specialist at the prime institutes of Saket and Laxmi Nagar. This training will provide you with an advanced degree of understanding of the subject of networking. On the other hand, learners who have a strong interest in the field of cybersecurity and ethical hacking will have the opportunity to participate in the 1 Year Diploma in Cybersecurity Course by Craw Security.
You can visit the Official Website of Craw Security to obtain additional information regarding the same courses, or you can give us a call at our 24-hour, seven-day-a-week hotline mobile number +91-9513805401 and speak with our highly skilled educational advisors.